ABA Clinic Requirements Checklist: What You Need for a Successful Practice

Understanding ABA Clinic Requirements
Launching an ABA clinic requires careful planning and a strong focus on providing high-quality care while adhering to legal and operational standards. This guide covers everything from education and licensing to insurance credentialing, staffing, and marketing, helping you build a thriving practice.
Applied behavior analysis (ABA) therapy is a proven approach for improving behavioral patterns, especially for individuals with autism spectrum disorder and other developmental challenges. Setting up an autism clinic involves navigating essential areas like legal requirements, insurance reimbursements, and hiring skilled ABA therapists.
Key steps in launching an ABA clinic include obtaining necessary licenses, tax IDs, and liability insurance, along with creating a solid business plan outlining goals, financial projections, and service offerings. A well-structured business plan also helps secure funding, whether through private investors, loans, or grants. Choosing a suitable location for your clinic is critical for both client engagement and operational efficiency.
Staffing plays a vital role in clinic success. ABA therapists should be trained, certified, and experienced, with ongoing professional development to stay current with industry best practices. Additionally, insurance credentialing is essential for making therapy accessible and ensuring smooth reimbursement processes. Marketing strategies, including digital outreach and referral programs, will help grow the clinic’s client base.
By focusing on legal compliance, business planning, quality staffing, and strategic growth, ABA clinics can create a strong foundation for long-term success in providing effective services.

Educational & Certification Requirements for ABA Providers
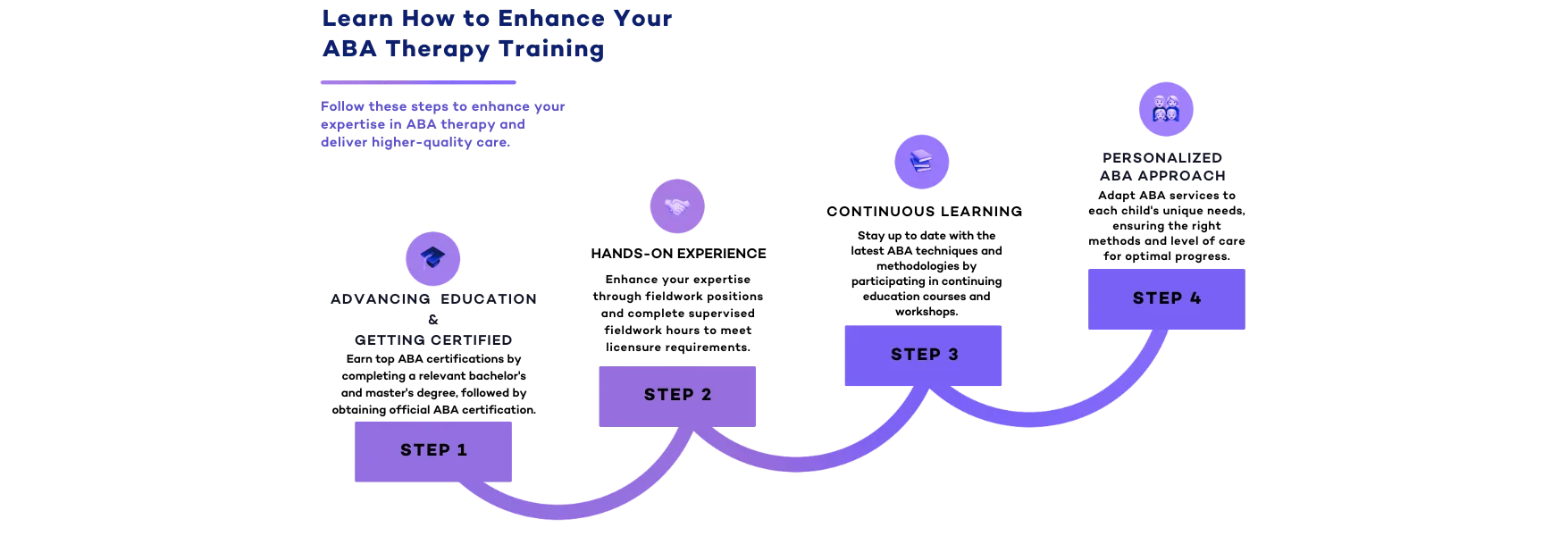
To provide ABA therapy, practitioners must meet specific educational and certification requirements. Applied behavior analysis relies on a scientifically proven approach to improving behavioral patterns, particularly for individuals with autism spectrum disorder and other developmental disorders. Those interested in entering this field must complete formal education, gain practical experience, and obtain certification to ensure they meet industry standards.
Education & Certification Pathway
Bachelor’s Degree: The First Step
The journey to becoming an ABA therapist begins with earning a bachelor’s degree in psychology, education, or a related field. This foundational step provides a strong understanding of human behavior, learning theories, and research methodologies—critical components for success in ABA programs. While a bachelor’s degree alone does not qualify someone to practice as a Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA), it is often enough to work as a Registered Behavior Technician (RBT) or an assistant behavior analyst under supervision.
Master’s Degree: Advancing Toward BCBA Certification
To become a Board Certified Behavior Analyst (BCBA), a master’s degree in behavior analysis, psychology, or a related field is required. Many accredited ABA programs offer coursework aligned with certification requirements set by the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB). A master’s degree not only expands a provider’s expertise but also opens doors for leadership roles, higher salaries, and the potential to start their own ABA practice.
BCBA Certification Exam: The Key to Professional Practice
After completing a master’s degree, aspiring ABA therapists must pass the BCBA certification exam. This rigorous test assesses knowledge of behavioral principles, ethical guidelines, and intervention strategies. Certification ensures that professionals meet the highest standards in ABA therapy, making them qualified to design and implement effective treatment plans.
Practical Experience: Gaining Hands-On Training
Before taking the BCBA certification exam, candidates must complete supervised fieldwork. Practical experience is an essential aspect of professional training, allowing future ABA therapists to apply their knowledge in real-world settings. Many ABA programs require candidates to work under the supervision of a certified BCBA, gaining expertise in treatment planning, data collection, and behavior improvement strategies.
Business Ownership: Opening Your Own ABA Clinic
For those interested in entrepreneurship, obtaining a BCBA certification and gaining experience can lead to opportunities in business ownership. Opening a clinic requires more than just clinical expertise—it also involves developing a solid business plan, securing funding, and understanding regulatory requirements. Many ABA professionals transition into private practice, allowing them to create tailored ABA therapy programs while maintaining control over their clinic’s operations.
The Role of Professional Organizations
Organizations such as Behavior Analysis International and the BACB oversee certification and ethical standards for the profession. They provide resources, continuing education opportunities, and guidelines that help ABA therapists maintain high-quality care. These organizations also support professionals who want to advance their careers, whether by specializing in a niche area of behavior analysis or by pursuing business ownership in the ABA field.
By following this structured educational and certification pathway, aspiring professionals can successfully navigate the steps needed to provide high-quality ABA therapy, whether working for an established practice or opening their own ABA practice.
Legal & Licensing Requirements for ABA Clinics
Choosing the Right Business Structure
Selecting the appropriate legal structure is crucial for protecting personal and business assets while ensuring smooth operations. When opening your own clinic, understanding the different business structures will help set the foundation for long-term success. Options include:
- Limited Liability Company (LLC): An LLC offers protection of personal assets while providing flexibility in management and taxation. It’s a common choice for ABA therapy clinic owners, separating personal and business liabilities and shielding individual finances from potential legal claims.
- Corporation (S-Corp or C-Corp): Larger ABA clinics may opt for a corporate structure, which allows for scalability, tax benefits, and easier access to investment. However, corporations require more complex administrative and tax filings.
- Sole Proprietorship: This option is the simplest to set up but doesn’t offer liability protection. Owners are personally responsible for business debts, making it riskier.
- Business Model Considerations: Deciding whether your clinic will be out-of-pocket, insurance-based, or hybrid is crucial. Insurance models may require credentialing with payers, while out-of-pocket offers flexibility but may limit accessibility.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) Guidelines: The SBA offers resources for structuring and funding an autism clinic. Their guidelines help owners with financing, tax obligations, and legal requirements for healthcare practices.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): This IRS-issued number is required for tax and payroll purposes. ABA therapy clinics with staff need an EIN to process wages, file taxes, and open a business bank account.
Licensing & Accreditation
Clinics must meet strict licensing and accreditation standards to ensure ABA compliance with industry regulations and to provide high-quality care to their clients. Maintaining proper licensing is critical for accepting clients and operating legally.
- Behavior Analysis Certification Board (BACB): This is the primary certification body for ABA therapists and clinic owners. The BACB ensures that professionals meet educational, training, and ethical standards required for providing ABA therapy services. Many states require BACB certification for clinics to operate legally.
- State Licensure: While BACB certification is a national standard, many states have additional licensing requirements for ABA therapy clinics. Researching state-specific regulations is crucial to ensure full compliance before accepting patients.
- Accreditation & Compliance: Many ABA therapy clinics pursue accreditation from organizations such as the Behavioral Health Center of Excellence (BHCOE) to demonstrate a commitment to high-quality care and compliance with best practices. Some insurance companies may require accreditation before credentialing a clinic.
- Certification Exam & Compliance Requirements: Clinic owners and ABA therapists must stay up to date with continuing education, ethical guidelines, and compliance requirements to ensure their clinic maintains it’s licensed status. Non-compliance can lead to penalties or loss of licensure.
- Professional Organizations: Joining an organization like the Association for Behavior Analysis International (ABAI) can help ABA therapy clinic owners stay informed on changes in industry regulations and licensing requirements. Many organizations provide valuable resources for clinic owners looking to navigate the complexities of running their clinic while maintaining compliance.
By understanding and following these legal and licensing requirements, ABA therapy clinic owners can ensure their practice is fully compliant and positioned for long-term success.

Operational Setup
Selecting & Setting Up Your Clinic Space
The right physical space enhances the effectiveness of therapy and supports a positive therapeutic environment. A well-designed clinic provides both you and your team with an optimal setting for implementing Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) interventions while ensuring client comfort and engagement.
Clinic Space & Physical Space Requirements
When selecting a clinic space, it’s essential to hold ethical considerations on several key factors that directly impact the delivery of ABA therapy:
- Accessibility: Ensure that the clinic is ADA-compliant, making it easy for individuals with mobility challenges and caregivers to navigate the space comfortably.
- Privacy: Treatment rooms should allow for one-on-one and small-group interventions without distractions, protecting client confidentiality and fostering focused learning environments.
- Room for Intervention Strategies: The clinic should have designated spaces for structured learning, sensory-friendly areas, and space for play-based or naturalistic interventions. Flexibility is key in supporting behavior analysis strategies tailored to individual client needs.
- Safety Considerations: Given that many clients may engage in challenging behaviors, it’s important to have secure and hazard-free spaces to prevent injuries.
Therapeutic Environment
An ABA clinic should be designed to support individuals with developmental disabilities by creating a welcoming, structured, and predictable space. Elements like visual schedules, clear labeling, and minimal distractions help enhance therapy. A supportive environment that reinforces positive behavior and offers social learning opportunities is key to effective treatment.

Choosing the Right Technology for ABA Practice Management
Technology plays an integral role in modern ABA practice management. From streamlining administrative workflows to tracking client progress in real-time, adopting the right tools can significantly enhance efficiency while improving clinical outcomes. Selecting the right technology ensures both you and your staff can focus more on providing quality therapy and less on time-consuming paperwork.
Practice Management Software
ABA clinics rely on an all-in-one solution for scheduling, billing, and data tracking. A robust system should integrate these functionalities seamlessly to support compliance with the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB) and other regulatory requirements. AI-driven tools that allow automated appointment reminders, secure telehealth options, and efficient claims processing can significantly reduce administrative burdens.
Administrative Tasks Optimization
Administrative efficiency is crucial for reducing overhead costs and ensuring clinicians have more time to focus on therapy. Key aspects include:
- Automated billing and insurance claims processing to minimize errors and denials.
- Digital intake forms and electronic consents to streamline patient onboarding.
- Secure and HIPAA-compliant storage of client records to ensure privacy and accessibility.
By utilizing a sophisticated all-in-one ABA system, clinics can enhance service delivery, reduce operational inefficiencies, and maintain compliance with industry regulations.
Analyze Data for Better Outcomes
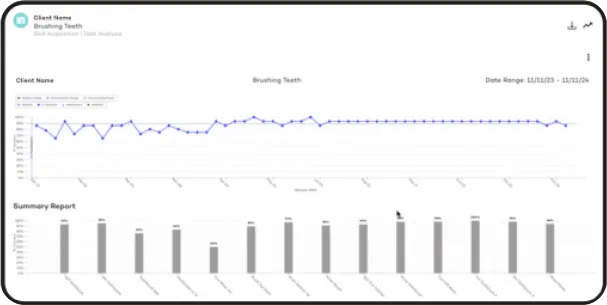
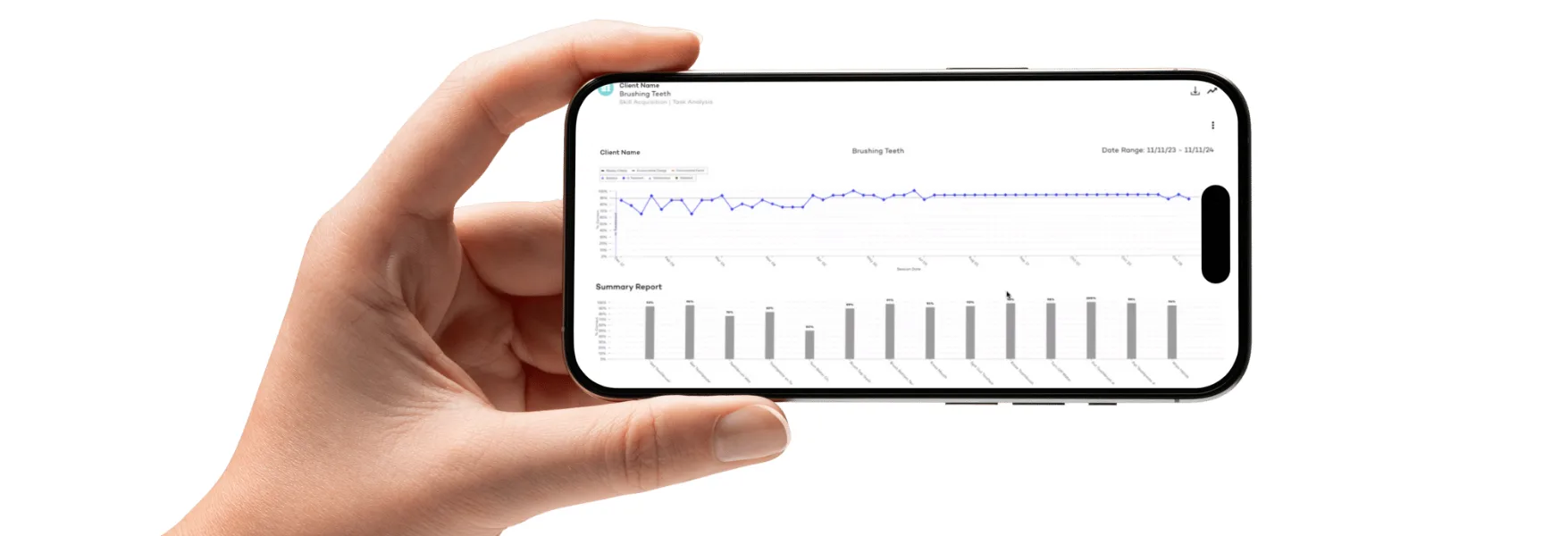
One of the biggest advantages of leveraging technology in an ABA practice is the ability to track and analyze client progress efficiently. A data-driven approach allows behavior analysts to make informed decisions about treatment plans, measure progress in real time, and adjust interventions accordingly.
Raven Health, for example, provides an intuitive platform designed to enhance data collection, reporting, and decision-making in ABA therapy. By offering real-time analytics and customizable reporting tools, Raven empowers clinicians to gain deeper insights into client progress, ensuring that therapy remains adaptive and evidence-based. With automated therapy session documentation and seamless integration with insurance requirements, Raven Health simplifies the complexities of practice management.
By adopting a comprehensive ABA practice management platform like Raven Health, clinics can enhance efficiency, support compliance with the Behavior Analyst Certification Board, and ultimately improve client outcomes.
Insurance Credentialing & Revenue Cycle Management
Credentialing with Insurance Companies
For new and rising clinics, credentialing with insurance companies is a crucial step in ensuring accessibility for families relying on reimbursements. The process can be complex, requiring careful attention to insurer-specific requirements, but successful credentialing opens the door to a wider client base and consistent revenue streams.
Insurance Providers & Private Insurance
Understanding the credentialing process with both private insurance companies and Medicaid providers is essential. Each insurer has distinct requirements, and meeting these conditions allows ABA providers to offer services that are financially accessible to more families.
- Provider Enrollment: The first step involves submitting an application to insurance provider networks, detailing qualifications and clinic credentials.
- Verification Process: Insurers conduct background checks, verifying professional licenses, certifications, and work history.
- Approval & Contracting: Once approved, providers negotiate reimbursement rates and agree to contractual terms, establishing long-term financial viability.
Credentialing Requirements
Each insurance company follows specific protocols, requiring providers to meet eligibility criteria, such as:
- Compliance with Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB) guidelines.
- Proof of licensure and liability insurance.
- Submission of National Provider Identifier (NPI) and Tax Identification Number (TIN).
Successfully navigating credentialing enhances a clinic’s credibility while ensuring families receive coverage for ABA services.
Medical Billing & Insurance Reimbursement
A strong revenue cycle is the backbone of financial stability for any clinic. Streamlined billing processes ensure steady cash flow, reducing administrative burdens and payment delays.
Insurance Reimbursements & Cash Flow
ABA billing training is a crucial must. Billing inefficiencies can lead to claim denials, reimbursement delays, and revenue loss. Implementing an optimized system ensures:
- Faster Claims Processing: Proper coding and claim submission reduce denials and accelerate payments.
- Reduced Financial Strain: Timely reimbursements support clinic operations and staff salaries.
- Automated Payment Tracking: Technology solutions, like Raven Health, helps providers manage invoices and monitor revenue cycles with ease.
HIPAA Compliance & Data Security
Protecting client confidentiality is not just a legal requirement—it’s an ethical obligation. Autism clinics must adhere to federal regulations to safeguard sensitive information and maintain trust within the community.
HIPAA Training & Implementation
Ensuring staff is well-versed in HIPAA guidelines is critical. This includes:
- Secure handling of client records.
- Restricted access to confidential information.
- Regular compliance audits to prevent data breaches.
Securing Client Data & Electronic Records
In an era of digital documentation, implementing cybersecurity measures is a must. ABA clinics should use encrypted systems for:
- Electronic Health Records (EHR): Secure storage of therapy notes and client progress reports.
- Data Encryption & Access Controls: Protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
- Regular System Audits: Identifying vulnerabilities before they become security risks.

Hiring & Staffing
Building a team of highly qualified professionals is fundamental to delivering top-tier ABA services. Retaining skilled staff not only strengthens clinical outcomes but also fosters long-term business growth.
Key Roles & Certification Requirements
ABA clinics require a diverse range of professionals, including:
- ABA Therapists & Experienced ABA Therapists: Directly implement treatment plans under supervision.
- Board Certified Behavior Analysts (BCBA) & Certified Behavior Analyst BCBA: Design and oversee behavioral analysis through intervention programs.
- Professional Behavior Analysts: Provide clinical supervision and conduct behavioral assessments.
- Occupational Therapists & Speech-Language Pathologists: Complement ABA therapy with speech, sensory and motor skill interventions.
Comprehensive Assessments
Skilled professionals conduct evaluations to determine individualized treatment plans. These assessments guide therapy approaches, ensuring tailored interventions for each client.
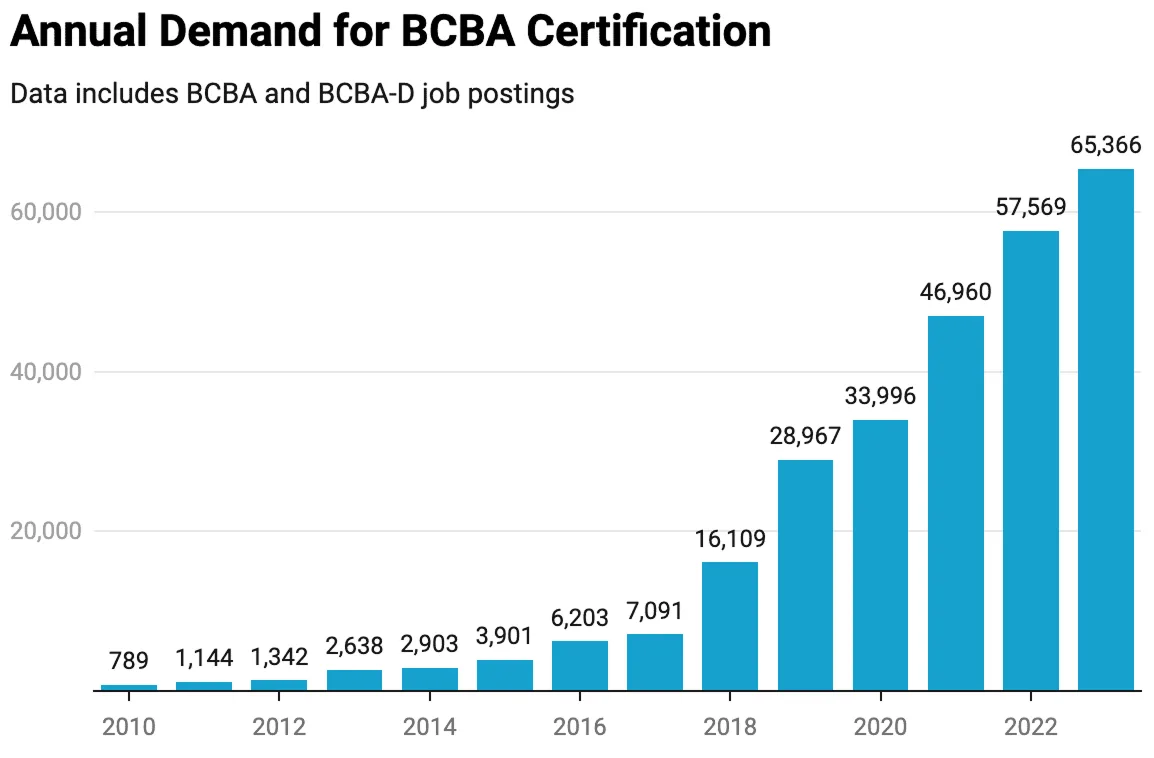
Recruiting & Retaining Skilled ABA Professionals
The demand for qualified ABA professionals is high, making recruitment and retention a priority.
Professional Associations & Networking
Building connections within the ABA community helps clinics attract top talent. Engaging with organizations like the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB) and attending industry events provide networking opportunities for recruitment.
Experienced ABA Therapists: Retention Strategies
- Competitive Salaries & Benefits: Offering comprehensive compensation packages encourages staff loyalty.
- Continuing Education Opportunities: Supporting professional development fosters employee satisfaction.
- Positive Work Environment: Encouraging collaboration and providing mentorship enhances job satisfaction.
Actively Listen: An Essential Hiring & Management Skill
For hiring managers and supervisors, active listening is crucial in understanding an ABA therapists needs, addressing concerns, and fostering a positive work culture.
Workers’ Compensation Insurance
Ensuring staff protection through proper workers’ compensation coverage is not only a legal obligation but also a way to support employees in case of workplace-related injuries.
Marketing & Growing Your Clinic
Strategic marketing efforts help emerging clinics expand their reach, attract new clients, and establish a strong presence in the community.
Creating an Effective Marketing Plan
A well-defined marketing plan helps position your clinic for success by focusing on:
- Target Market & Local Business Partnerships: Identifying key demographics and building relationships with local pediatricians, schools, and advocacy groups.
- Private Pay Considerations: While insurance plays a significant role, attracting private-pay clients can create additional revenue streams.
- Business & Marketing Investments: Leveraging available financial resources for online advertising, social media campaigns, and community outreach.
Expanding Your ABA Practice
Growth requires active engagement with potential clients and local organizations. By increasing visibility and credibility, clinics can establish themselves as trusted resources for ABA therapy.

Participating in Local Events & Community Engagement
Attending autism awareness events, school fairs, and parent support groups not only builds brand awareness but also establishes your clinic as a community leader in behavioral health.
Reaching Families in Need
Proactive outreach ensures that families seeking ABA services can find and trust your clinic. Strategies include:
- Social Media & Digital Marketing: Educational content and success stories build trust and engagement.
- Referral Networks: Collaborating with medical professionals and special education providers expands client outreach.
- Free Consultations & Workshops: Offering informational sessions to introduce families to ABA therapy and its benefits.
By leveraging effective marketing and operational strategies, new ABA clinics can thrive, providing invaluable services to children and families in need of behavior analysis interventions.
Final Thoughts: Ensuring Long-Term Success for Your ABA Clinic
Success in the ABA field requires ongoing commitment to compliance, professional growth, and patient-centered care.
- Entire Process Optimization: Refining operations for efficiency.
- Patient Outcomes & Effective Therapy: Focusing on quality care.
- Professional Growth: Encouraging continued education and development.
Using Raven Health for Your ABA Business
Starting and running a successful ABA clinic involves managing compliance, billing, and operational efficiency. Raven Health offers cutting-edge AI-driven practice management software designed to streamline administrative tasks and enhance patient outcomes. Take advantage of Raven Health’s free 30-day trial to optimize your ABA business today.